Eligibility for Surgery
Eligibility for Surgery

Bariatric Surgery
| Category | BMI range – kg/m2 |
| Very severely underweight | less than 15 |
| Severely underweight | from 15.0 to 16.0 |
| Underweight | from 16.0 to 18.5 |
| Normal (healthy weight) | from 18.5 to 25 |
| Overweight | from 25 to 30 |
| Obese Class I (Moderately obese) | from 30 to 35 |
| Obese Class II (Severely obese) | from 35 to 40 |
| Obese Class III (Very severely obese) | over 40 |
BMI
Do I Qualify?
Millions of people would like to lose weight. Severely obese patients are considered viable candidates to undergo bariatric surgery.
Severe obesity (Morbid Obesity) is defined by the patient’s body mass index, or ratio of fat to lean body mass. It is an equation that uses weight, height and age in the calculation.
Severe obesity is defined as weight that is at least 100 pounds more than the ideal body weight for a person’s height and age.
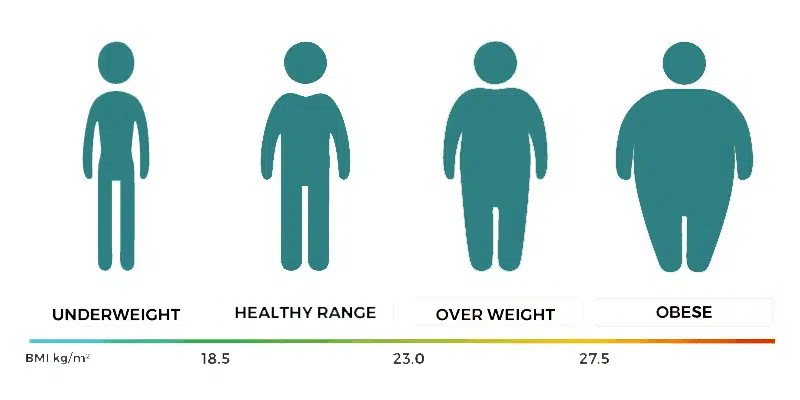

Bariatric surgery qualifications:
To qualify for any bariatric surgery, patients must typically:
- Have a minimum BMI of 40, or a minimum BMI of 35 with 2 or more significant medical diseases related to their obesity.
- Be between the ages of 18 and 60. Patients older or younger may be considered on a case-by-case basis.
- Your insurance provider may require you to show evidence of previous attempts to lose weight through a medically supervised program.
- Have been unsuccessful with organized weight loss attempts
- Be capable of and willing to adhere to all nutritional guidelines postoperatively
- Be able to demonstrate that they know what surgery is about, including risks and benefits, and that they understand the lifelong commitment to care after the surgery
- Have a supportive family with realistic expectations about weight loss surgery
Who is Not a Good Candidate?
- Have a medically correctable cause of obesity
- Current smokers
- Have had a substance abuse problem within the preceding year
- Have a medical, psychiatric or cognitive condition that would significantly impair their ability to adhere to diet, exercise or medication regimens
- Are currently breast-feeding, pregnant or planning to become pregnant within two years
Bariatric surgery has been proven to be more effective than nonsurgical treatments at achieving and maintaining long term and significant weight loss

Bariatric Surgery
Do I Qualify?
Millions of people would like to lose weight. Severely obese patients are considered viable candidates to undergo bariatric surgery.
Severe obesity (Morbid Obesity) is defined by the patient’s body mass index, or ratio of fat to lean body mass. It is an equation that uses weight, height and age in the calculation.
Severe obesity is defined as weight that is at least 100 pounds more than the ideal body weight for a person’s height and age.

| Category | BMI range – kg/m2 |
| Very severely underweight | less than 15 |
| Severely underweight | from 15.0 to 16.0 |
| Underweight | from 16.0 to 18.5 |
| Normal (healthy weight) | from 18.5 to 25 |
| Overweight | from 25 to 30 |
| Obese Class I (Moderately obese) | from 30 to 35 |
| Obese Class II (Severely obese) | from 35 to 40 |
| Obese Class III (Very severely obese) | over 40 |
BMI
Bariatric surgery qualifications:
To qualify for any bariatric surgery, patients must typically:
- Have a minimum BMI of 40, or a minimum BMI of 35 with 2 or more significant medical diseases related to their obesity.
- Be between the ages of 18 and 60. Patients older or younger may be considered on a case-by-case basis.
- Your insurance provider may require you to show evidence of previous attempts to lose weight through a medically supervised program.
- Have been unsuccessful with organized weight loss attempts
- Be capable of and willing to adhere to all nutritional guidelines postoperatively
- Be able to demonstrate that they know what surgery is about, including risks and benefits, and that they understand the lifelong commitment to care after the surgery
- Have a supportive family with realistic expectations about weight loss surgery
Who is Not a Good Candidate?
- Have a medically correctable cause of obesity
- Current smokers
- Have had a substance abuse problem within the preceding year
- Have a medical, psychiatric or cognitive condition that would significantly impair their ability to adhere to diet, exercise or medication regimens
- Are currently breast-feeding, pregnant or planning to become pregnant within two years
